Page 4
CMS-TOP-24-001

Page 1
Oct 9th, 2025
Page 2
CMS-MLG-24-002
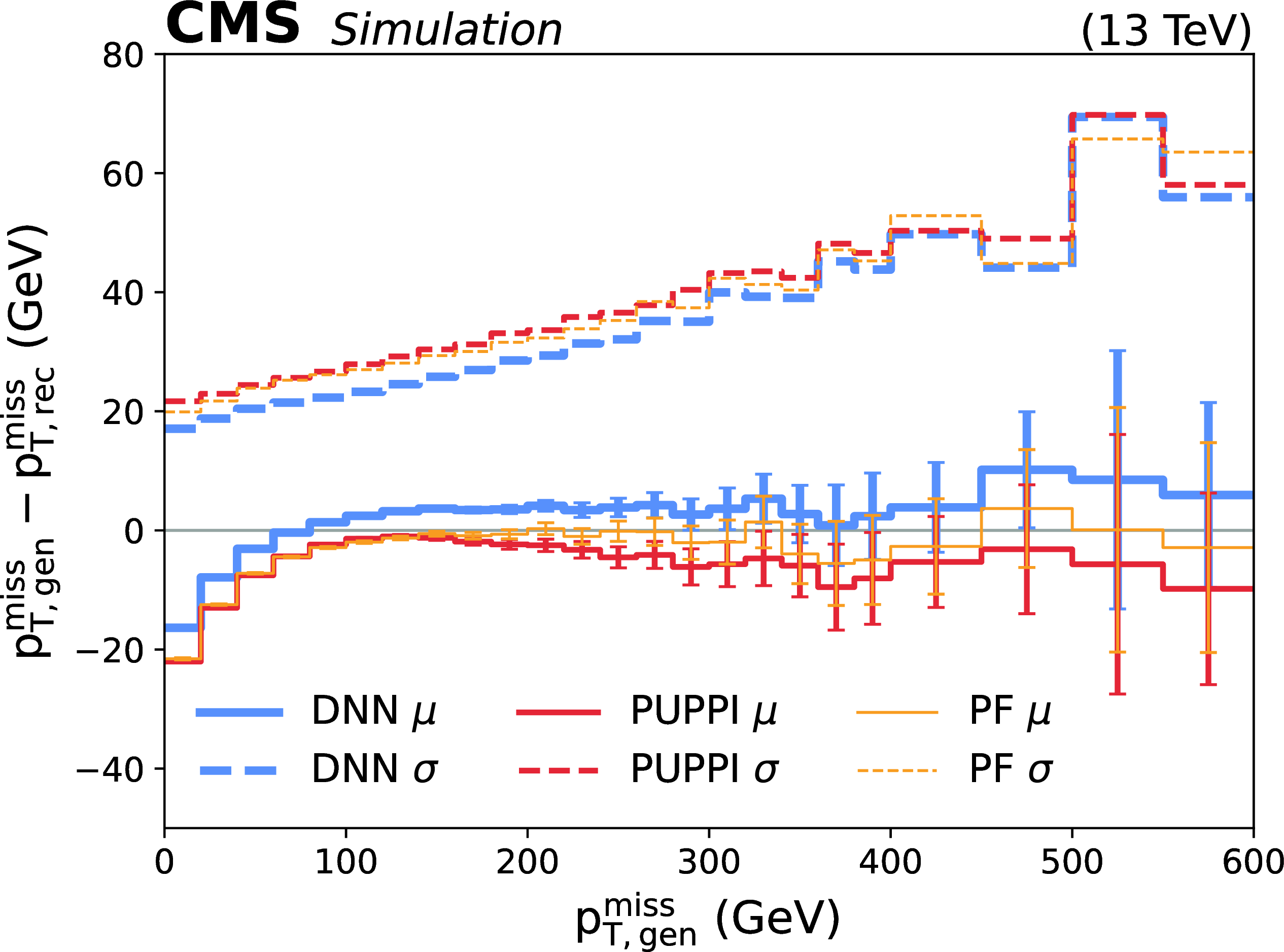
Wasserstein normalized autoencoder for anomaly detection
A novel anomaly detection algorithm is presented. The Wasserstein normalized autoencoder (WNAE) is a normalized probabilistic model that minimizes the Wasserstein distance between the learned probability distribution -- a Boltzmann distribution where the energy is the reconstruction error of the autoencoder -- and the distribution of the training data. This algorithm has been developed and applied to the identification of semivisible jets -- conical sprays of visible standard model particles and invisible dark matter states -- with the CMS experiment at the CERN LHC. Trained on jets of particles from simulated standard model processes, the WNAE is shown to learn the probability distribution of the input data in a fully unsupervised fashion, such that it effectively identifies new physics jets as anomalies. The model consistently demonstrates stable, convergent training and achieves strong classification performance across a wide range of signals, improving upon standard normalized autoencoders, while remaining agnostic to the signal. The WNAE directly tackles the problem of outlier reconstruction, a common failure mode of autoencoders in anomaly detection tasks.
Page 3
CMS-TOP-24-001
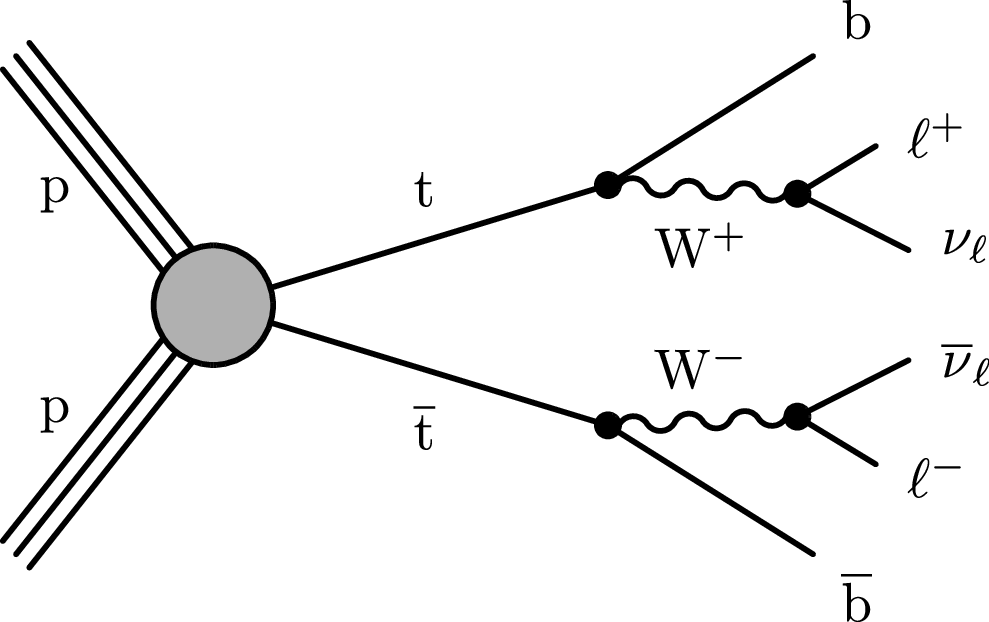
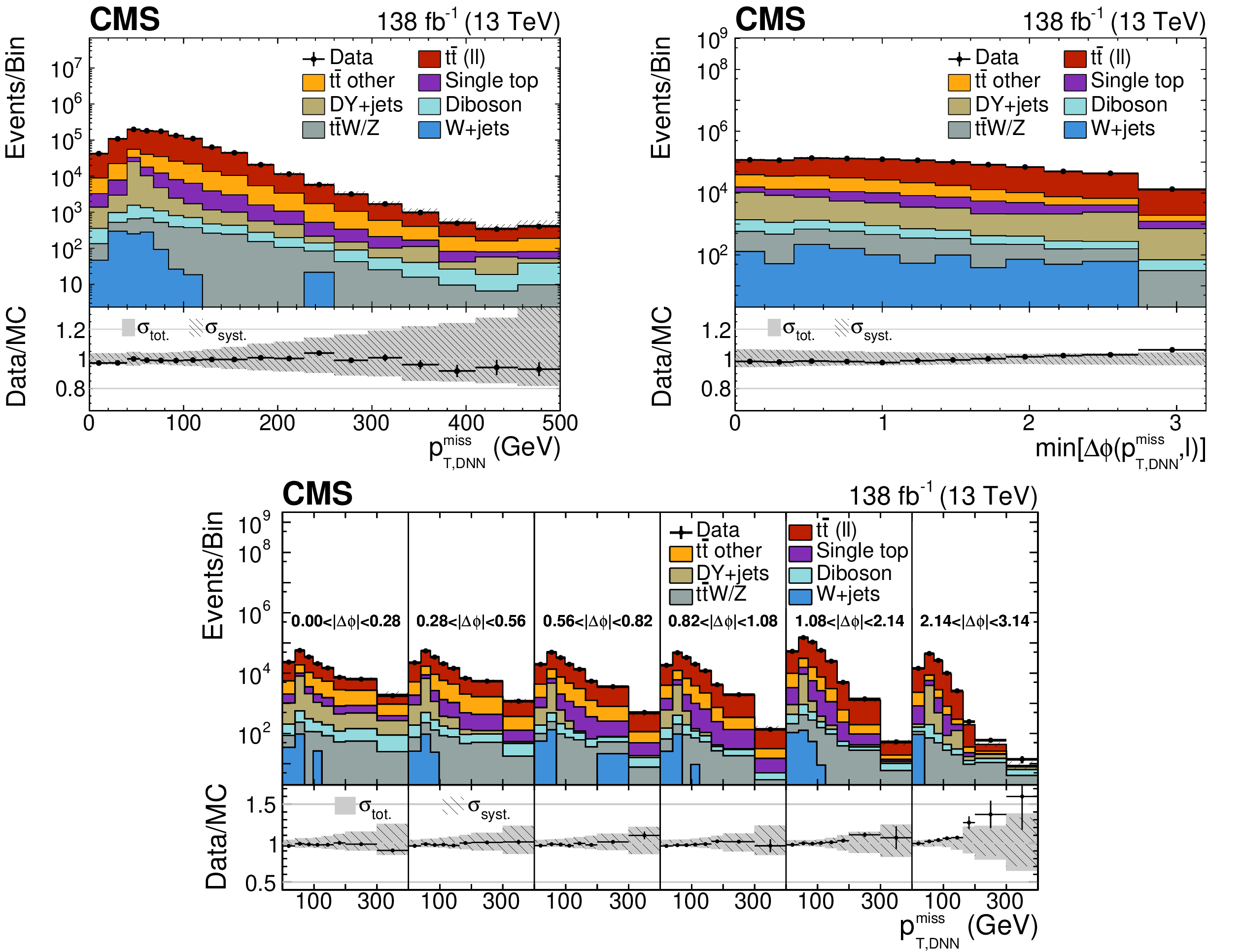
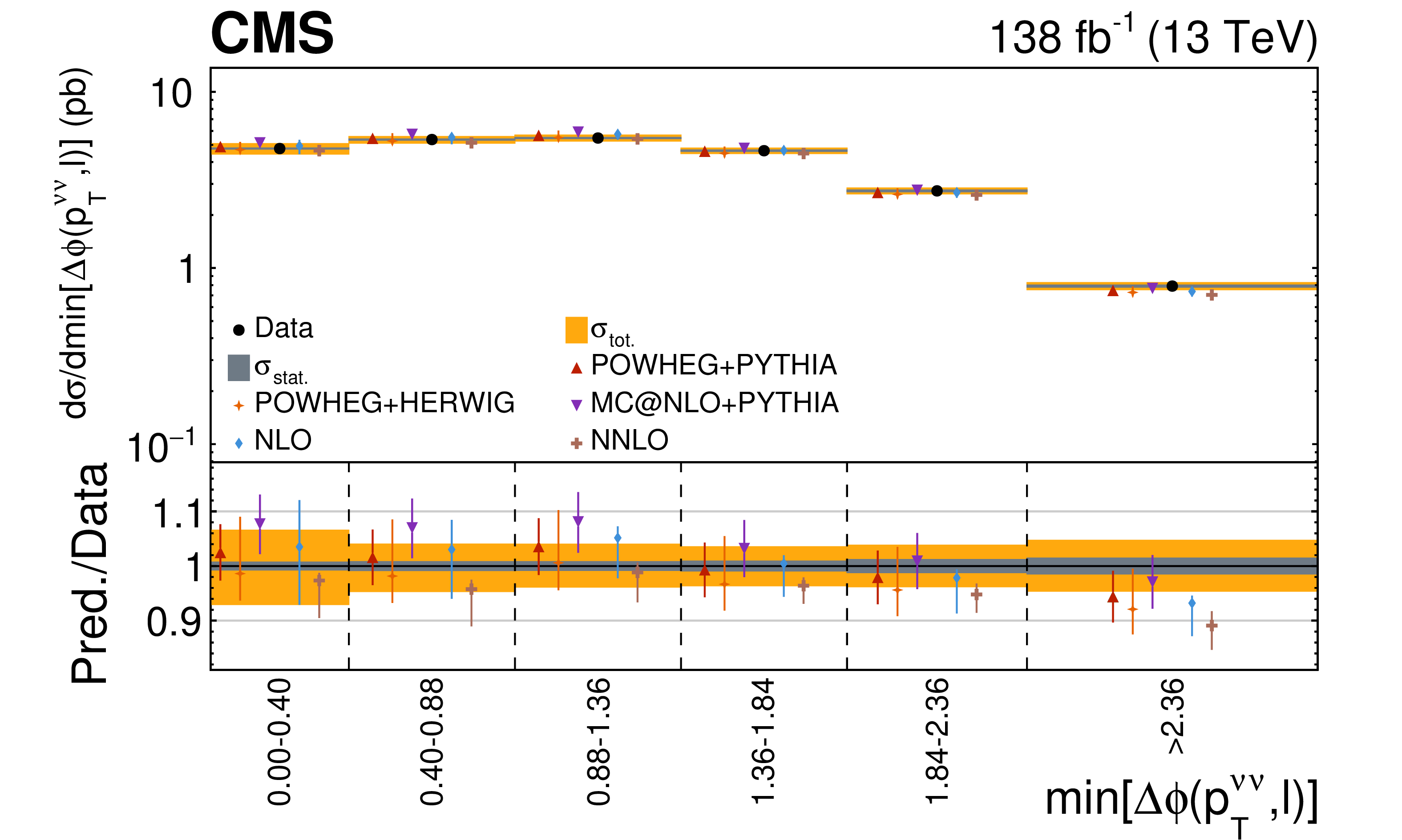
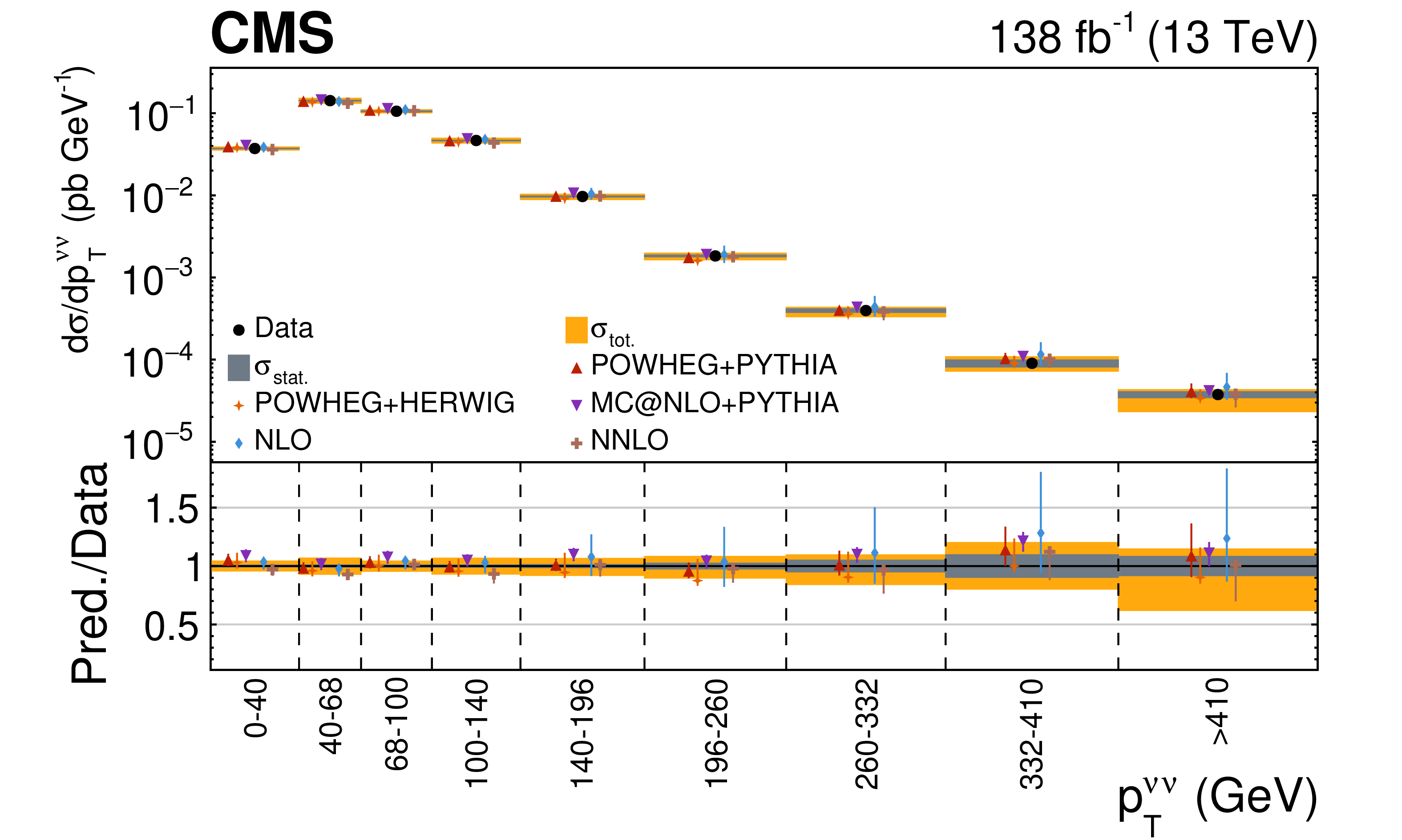
Measurement of the dineutrino system kinematic variables in dileptonic top quark pair production in proton-proton collisions at √s= 13 TeV
Differential top quark pair production cross sections are measured in the dilepton final states e+e−, μ+μ−, and e±μ∓, as a function of kinematic variables of the two-neutrino system: the transverse momentum pTνν of the dineutrino system, the minimum distance in azimuthal angle between vec(pTνν) and leptons, and in two dimensions in bins of both observables. The measurements are performed using CERN LHC proton-proton collisions at √s= 13 TeV, recorded by the CMS detector between 2016 and 2018, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb−1. The measured cross sections are unfolded to the particle level using an unregularized least squares method. Results are compared with predictions by the standard model of particle physics, and found to be in agreement with theoretical calculations as well as Monte Carlo simulations.
Page 4
CMS-TOP-24-001



Page 5
CMS-TOP-24-001
Page 6
CMS-TOP-24-001
Page 7
CMS-SMP-22-011
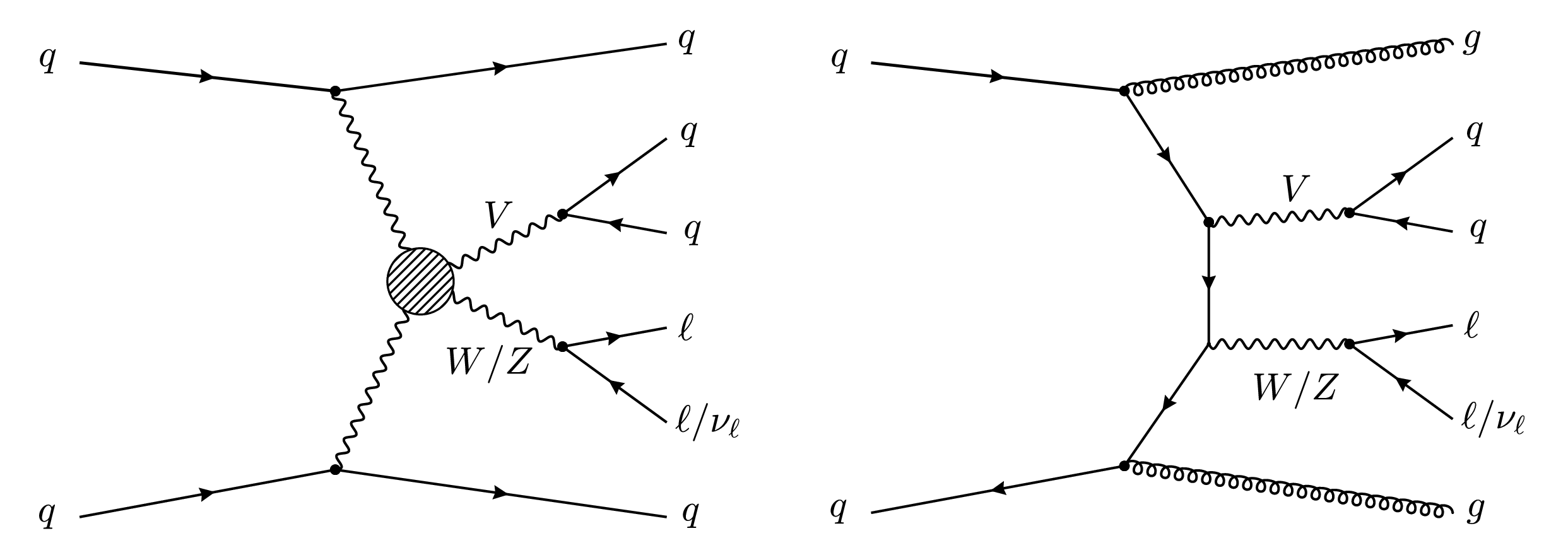
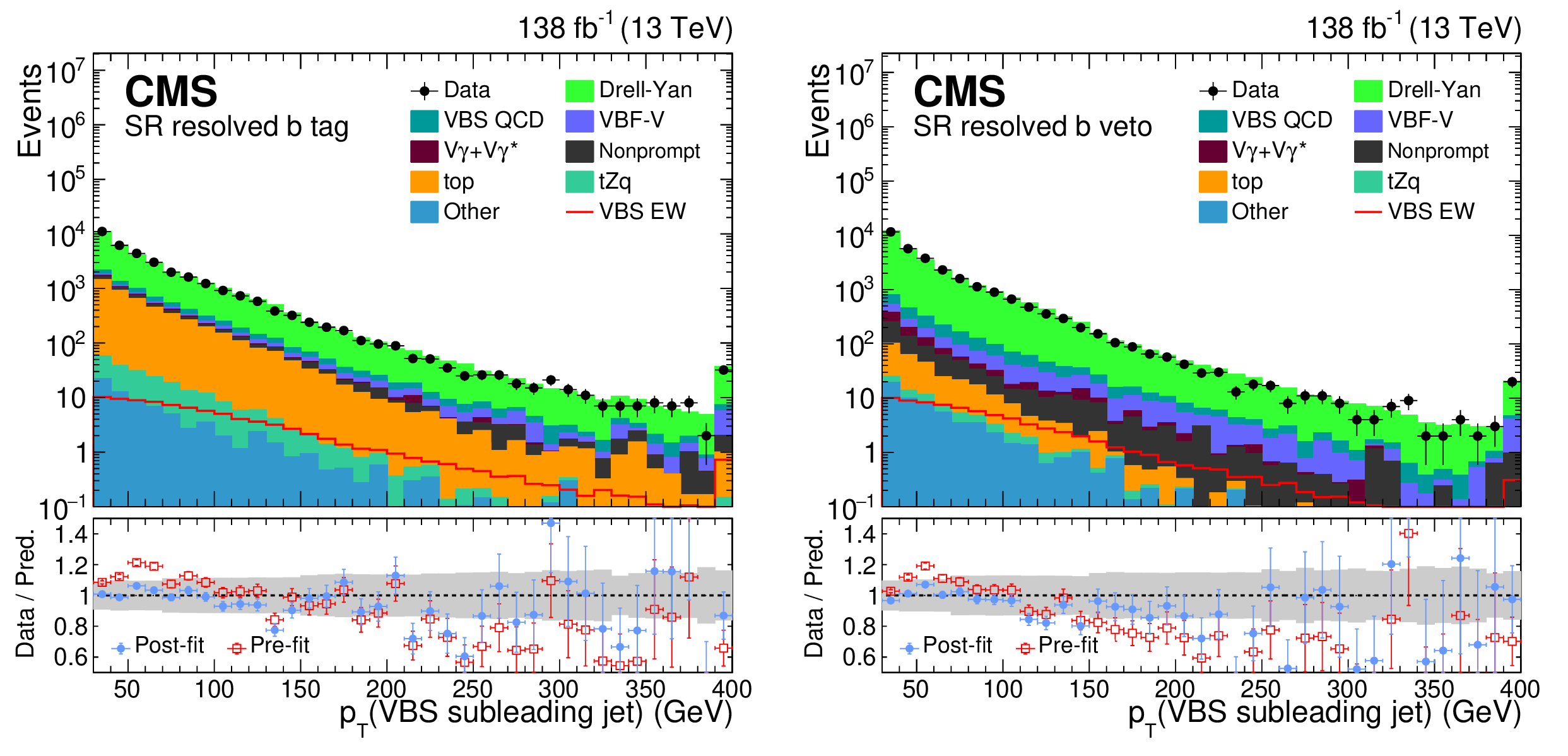
Vector boson scattering and anomalous quartic couplings in final states with ℓνqq or ℓℓqq plus jets using proton-proton collisions at √s= 13 TeV
A measurement is presented of the electroweak vector boson scattering production of ZV (V = W, Z) boson pairs associated with two jets in proton-proton collisions at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV. The data, corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 138 fb−1, were collected at the CERN LHC with the CMS detector during the 2016--2018 data-taking period. The analysis targets final states with a pair of isolated electrons or muons from Z boson decays and three or four jets, depending on the momentum of the vector boson that decays into quarks. Signal strength is measured for events characterized by a large invariant mass of two forward jets with a wide pseudorapidity gap between them. The electroweak production of ZV in association with two jets is measured with an observed (expected) significance of 1.3 (1.8) standard deviations. A combination of the analyses of ZV channel and the previously published WV channel in the lepton plus jets final state places constraints on effective field theory parameters that describe anomalous electroweak production of WW, WZ, and ZZ boson pairs in association with two jets. Several world best limits are set on anomalous quartic gauge couplings in terms of dimension-8 standard model effective field theory operators.
Page 8
CMS-SMP-22-011
Page 9
CMS-SMP-22-011
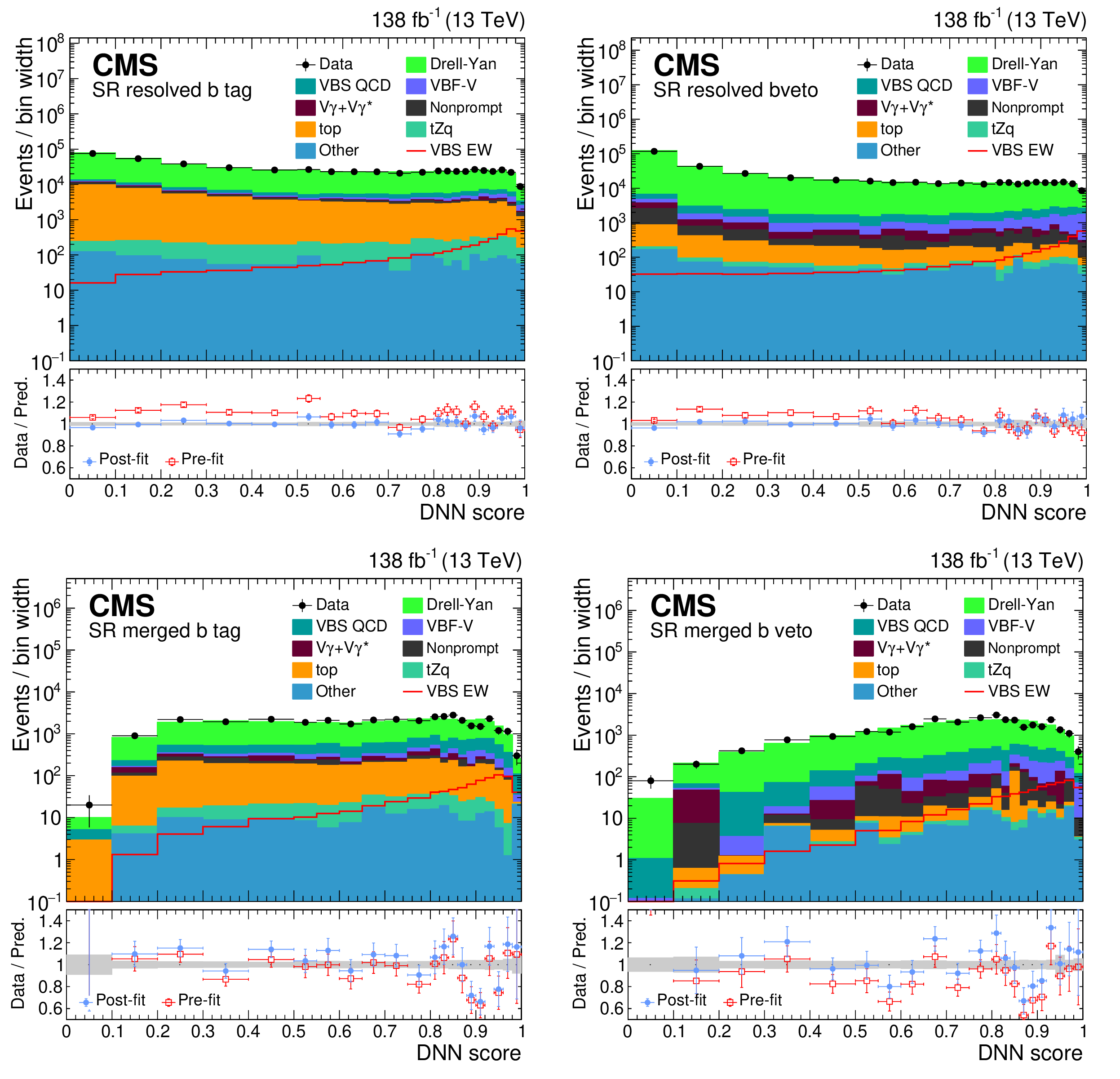
Page 10
CMS-SMP-22-011
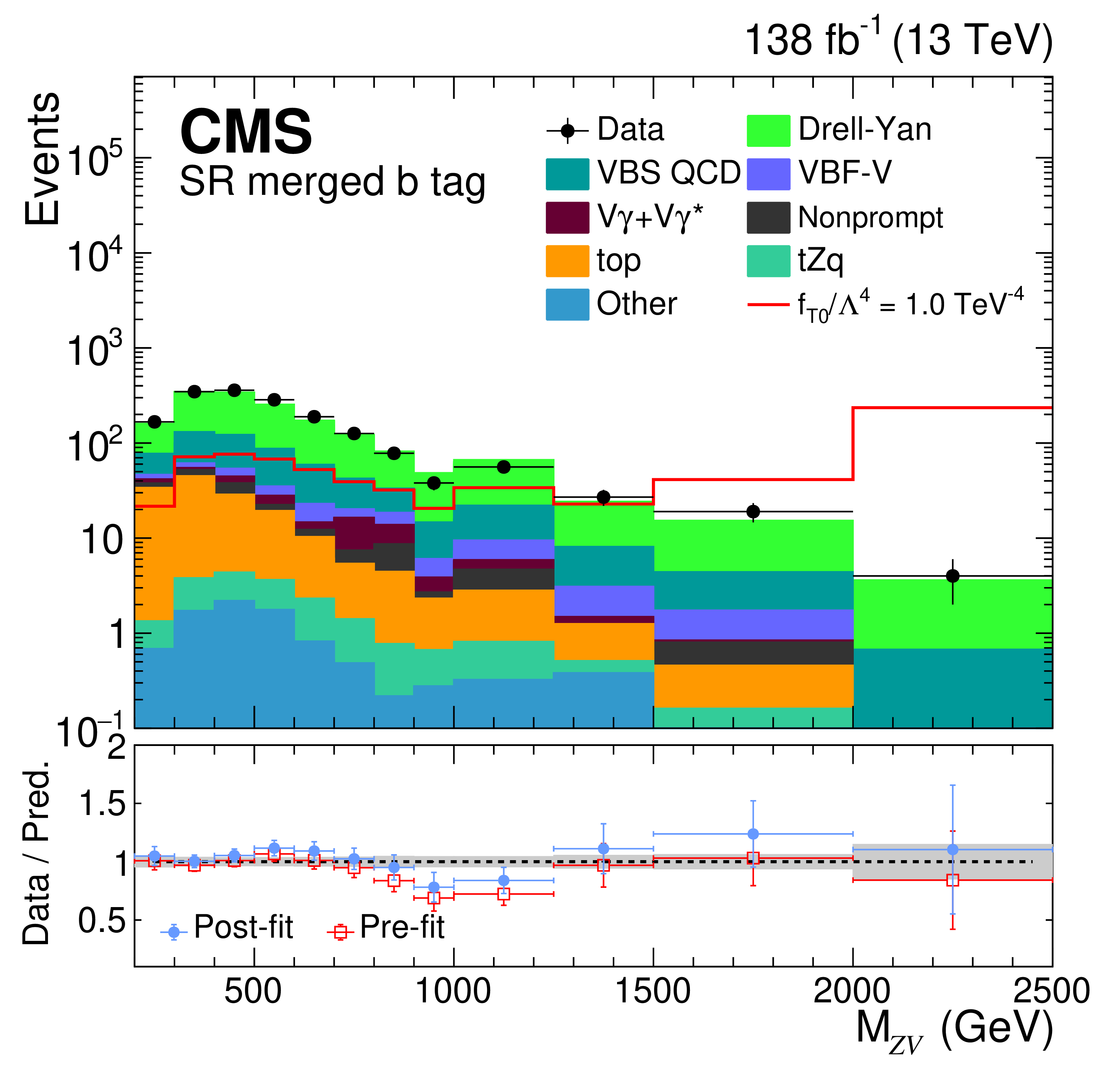
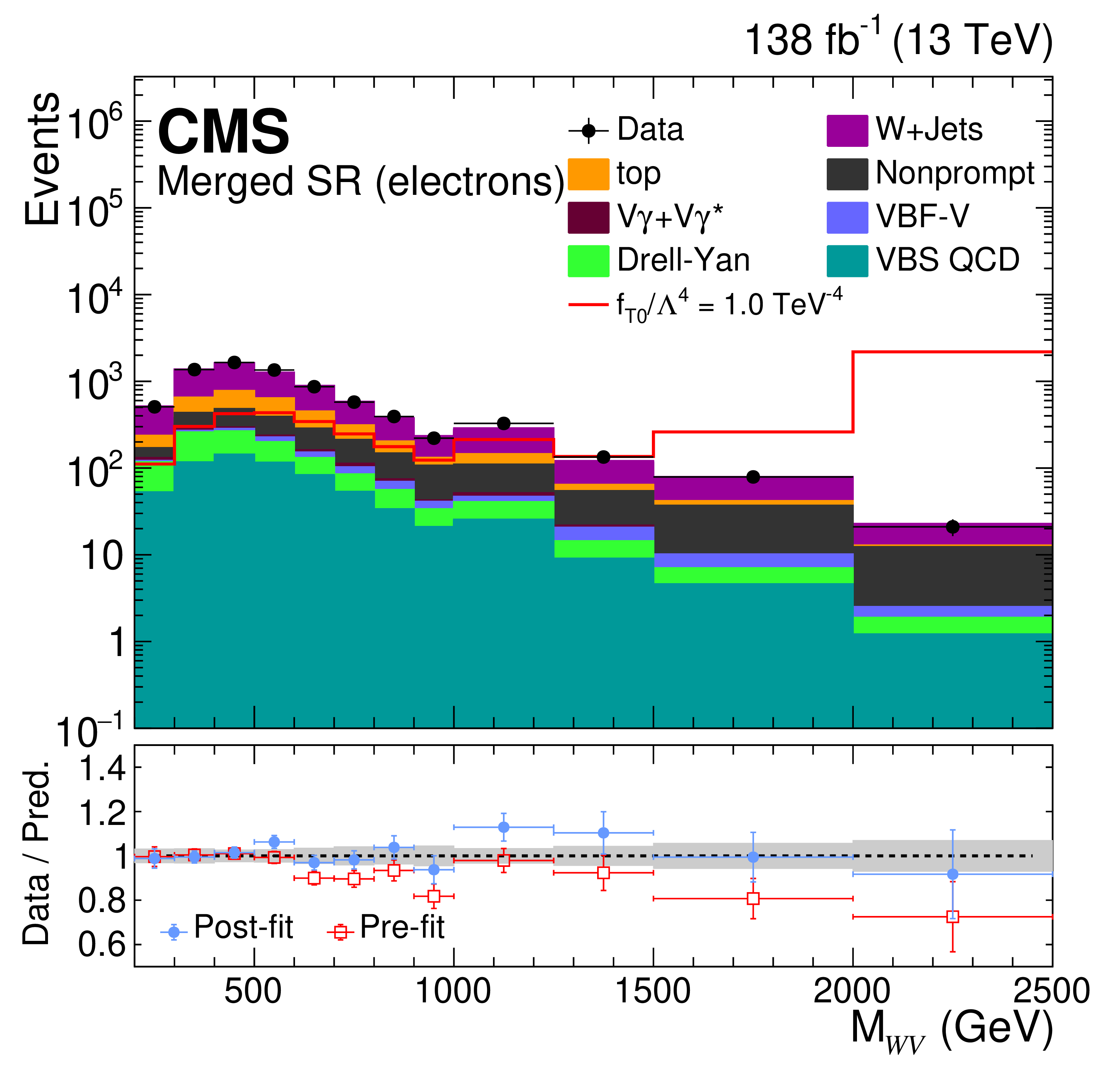
Page 11
The REDTOP experiment: a η/η’ factory to explore dark matter and physics beyond the Standard Model
M. Zielinski, C. Gatto
The REDTOP experiment is a proposed super-η/η’ factory aimed at exploring physics beyond the Standard Model in the MeV-GeV range and rare η/η’ meson decays. With projected production rates exceeding 1013 η/year and 1012 η’/year, REDTOP will enable studies of symmetry violations and all four portals to the Dark Sector. Preliminary studies show sensitivity, which could open a broad possibility for exploring new physics and contribute to a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions within the Standard Model. Such high statistics experiments and the required sensitivity can only be achieved with a high intensity proton or pion beam, available at several accelerator facilities worldwide. This article discusses the physics potential of the REDTOP experiment, the detector design, and the future beam requirements.
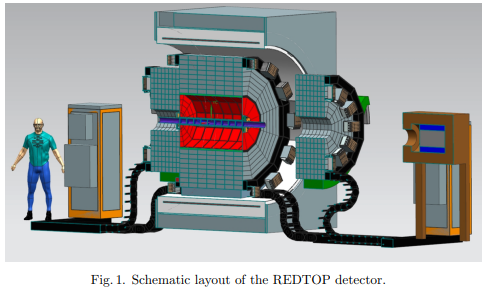
Page 12
Efficient tau-pair invariant mass reconstruction with simplified matrix element techniques
A. Kalinowski, W. Matyszkiewicz
The quality of the invariant mass reconstruction of the di-τ system is crucial for searches and analyses of di-τ resonances. Due to the presence of neutrinos in the final state, the ττ invariant mass cannot be calculated directly at hadron colliders, where the longitudinal momentum sum constraint cannot be applied. A number of approaches have been adopted to mitigate this issue. The most general one uses Matrix Element (ME) integration for likelihood estimation, followed by invariant mass reconstruction as the value maximizing the likelihood. However, this method has a significant computational cost due to the need for integration over the phase space of the decay products. We propose an algorithm that reduces the computational cost by two orders of magnitude, while maintaining the resolution of the invariant mass reconstruction at a level comparable to the ME-based method. Moreover, we introduce additional features to estimate the uncertainty of the reconstructed mass and the kinematics of the initial τ leptons (e.g., their momenta).
Page 13
BES-III Collab.
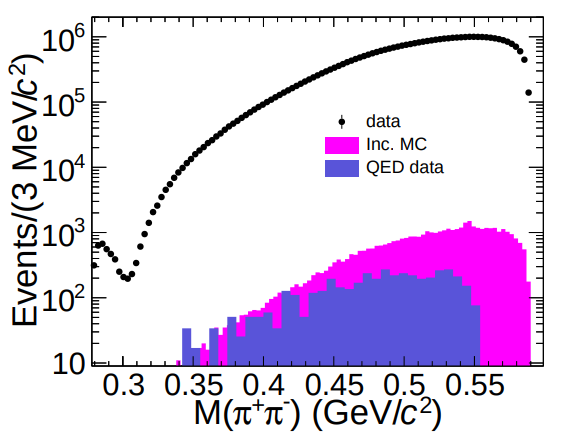
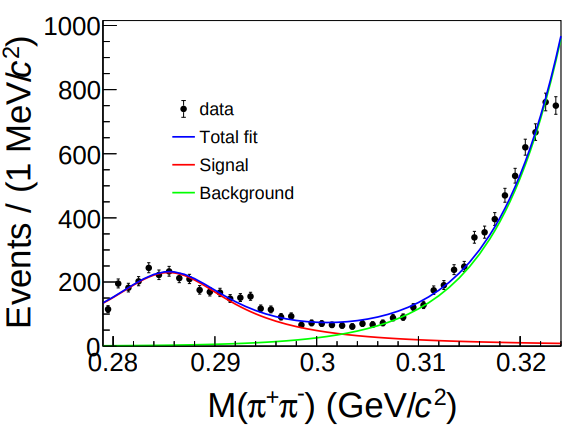
Observation of a resonance-like structure near the π+π- mass threshold in ψ(3686) → π+π- J/ψ
Based on the (2712.4 ± 14.4) x 106 ψ(3686) events collected with the BESIII detector, we present a high-precision study of the π+π- mass spectrum in ψ(3686)→ π+π- J/ψ decays. A clear resonance-like structure is observed near the π+π- mass threshold for the first time. A fit with a Breit-Wigner function yields a mass of 285.6 ±2.5 MeV/c2 and a width of 16.3 ±0.9 MeV with a statistical significance exceeding 10σ. To interpret the data, we incorporate final-state interactions (FSI) within two theoretical frameworks: chiral perturbation theory (ChPT) and QCD multipole expansion (QCDME). ChPT describes the spectrum above 0.3 GeV/c2 but fails to reproduce the threshold enhancement. In contrast, the QCDME model, assuming the ψ(3686) is an admixture of S- and D-wave charmonium, reproduces the data well. The pronounced dip near 0.3 GeV/c2 offers new insight into the interplay between chiral dynamics and low-energy QCD.
Page 14
BES-III Collab.
Page 15
ATLAS Collab.
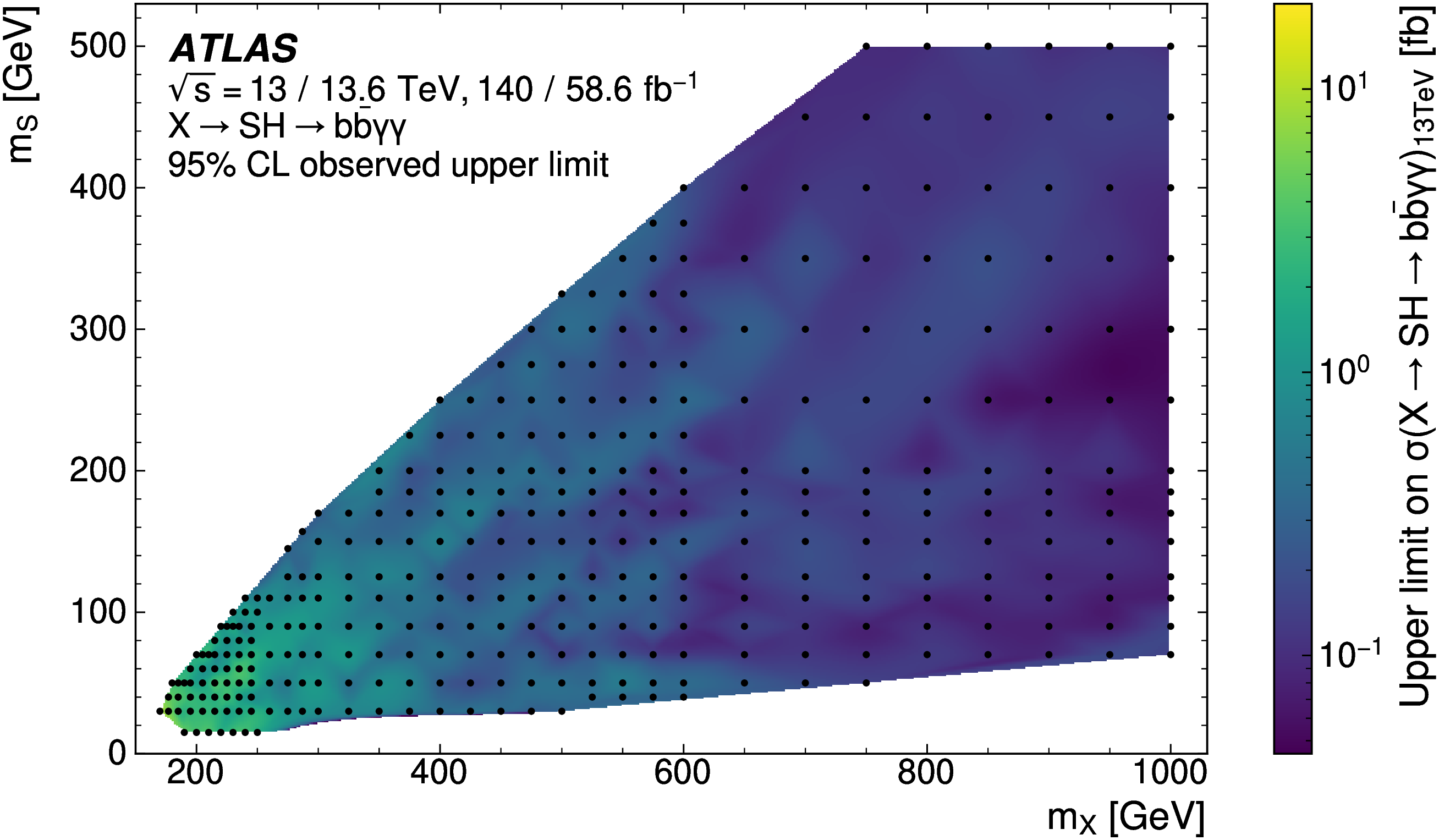
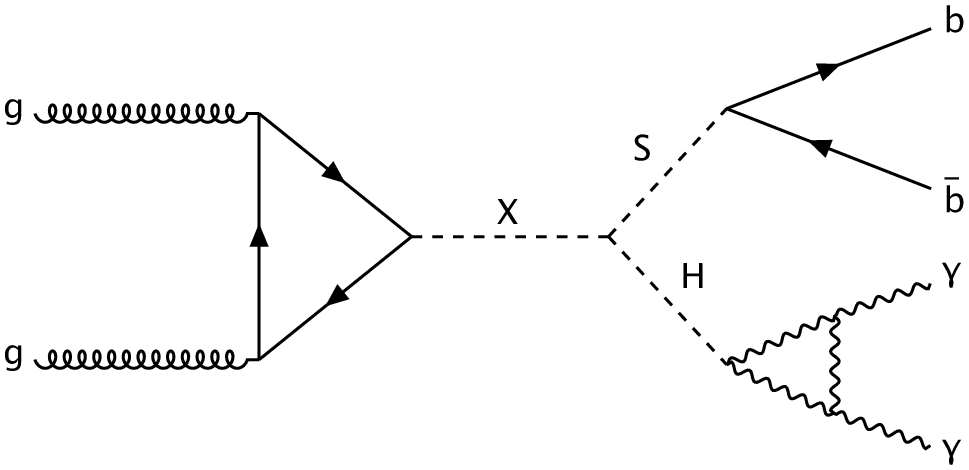
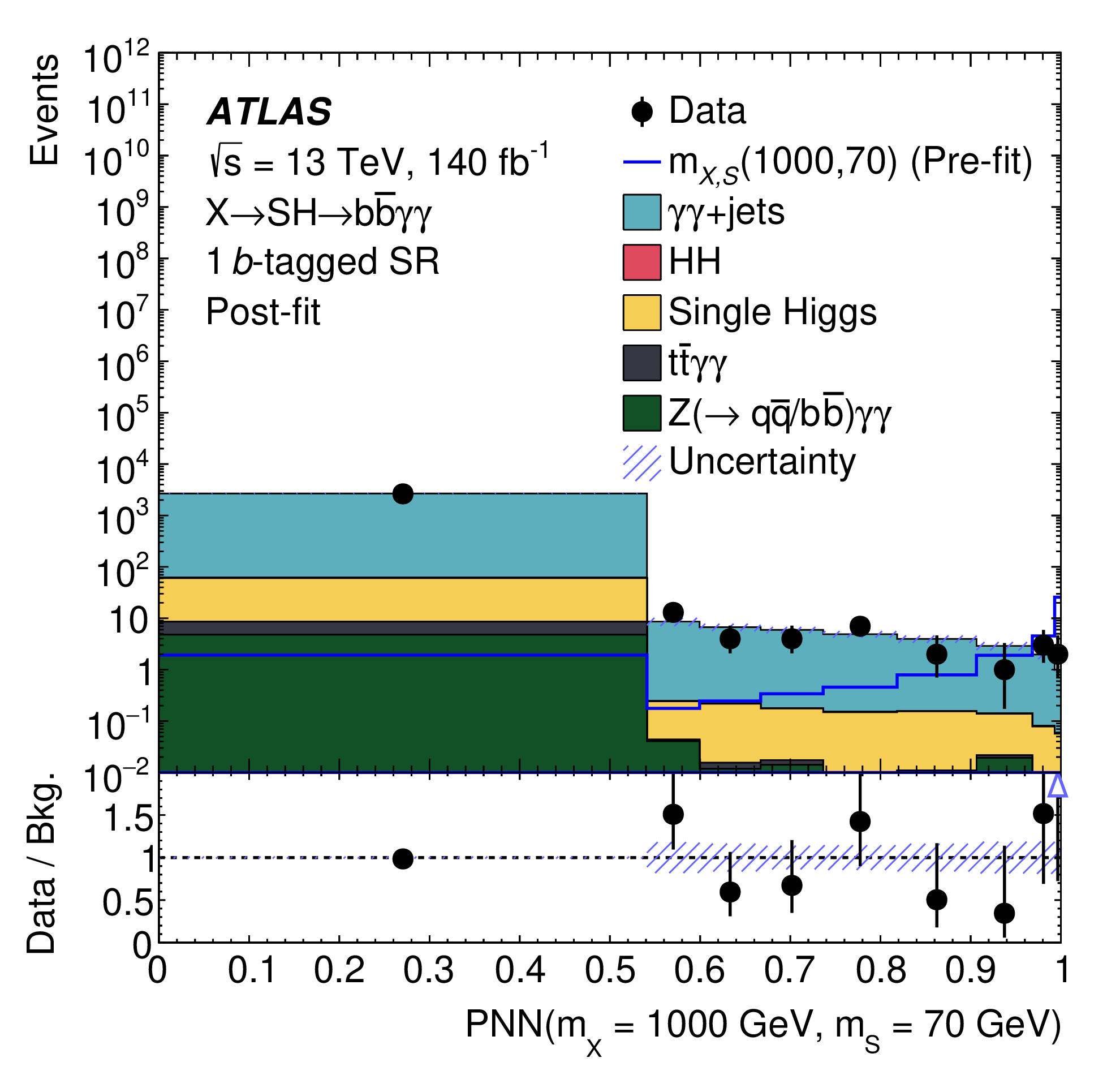
Search for a resonance decaying into a scalar particle and a Higgs boson in the final state with two bottom quarks and two photons with 199 fb of data collected at √s =13 TeV and √s =13.6 TeV with the ATLAS detector
A search for the resonant production of a heavy scalar X decaying into a Higgs boson and a lighter scalar S, through the process X→S(→bb)H(→γγ), where the two photons are consistent with the Higgs boson decay, is performed. The search is conducted using integrated luminosities of 140 fb-1 and 58.6 fb-1 of proton-proton collision data at centre-of-mass energies of 13 TeV and 13.6 TeV respectively, recorded with the ATLAS detector at the Large Hadron Collider. The search is performed over the mass ranges of 170 < mX <1000 GeV and 15 < mS < 500 GeV. No significant excess over the Standard Model background prediction is observed and limits at 95% confidence level are set on the cross-section times branching ratio σ(X→S(→bb)H(→γγ)) at 13 TeV, ranging from 9 fb to 0.06 fb.
Page 16
ATLAS Collab.
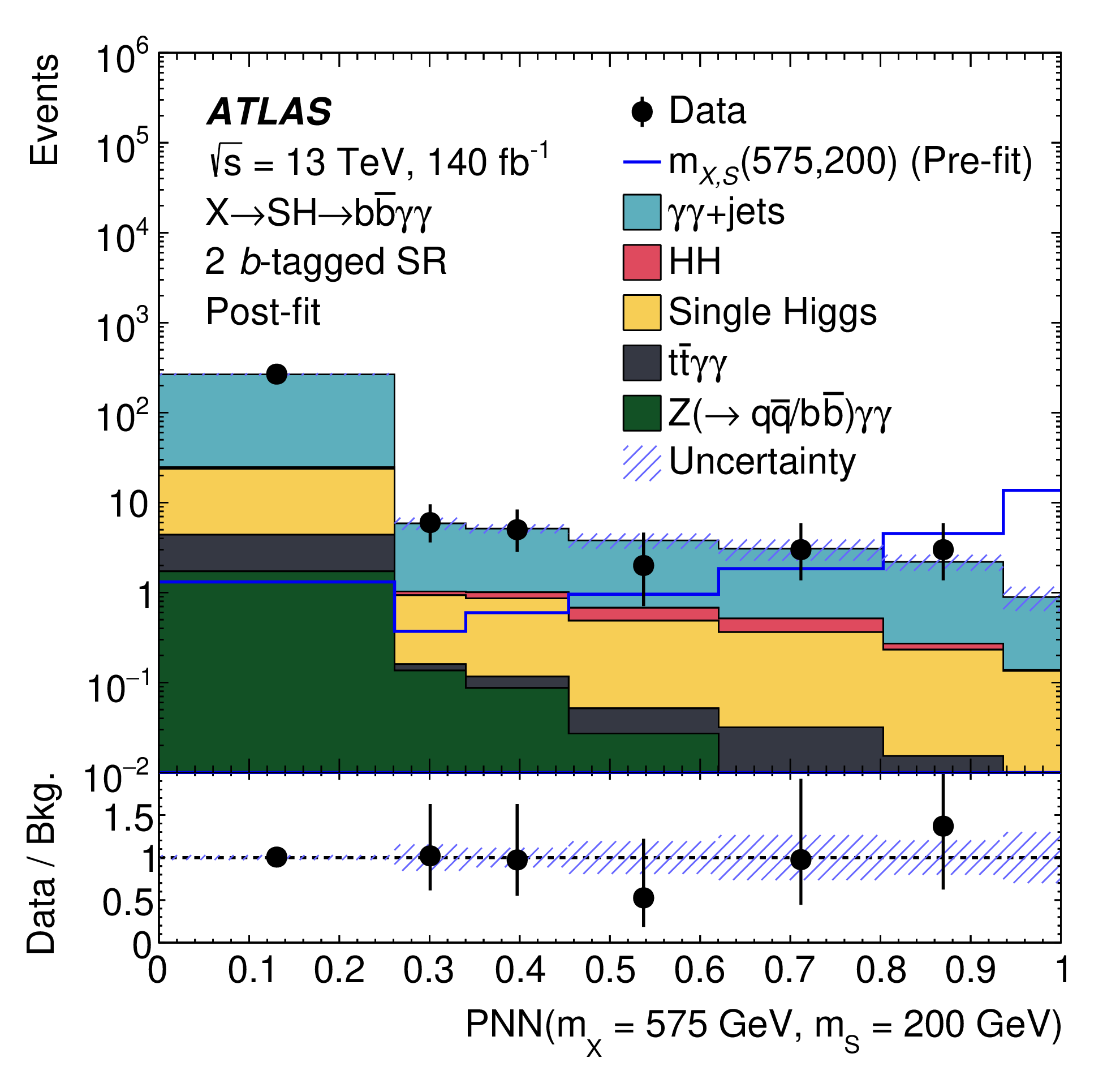
Page 17
ATLAS Collab.